- Introduction
- 1. React Native Internals 📡
- 2. Setting up the project 🌈
- 3. See it in action! 🎬
- 4. Project Structure 🏢
- 5. Conventions and Code Style 🎓
- 6. Testing and Debugging 🚫🐞
- 7. Styling 💅🏻
- 8. Redux 🗄
- 9. Navigation 🚪
- 10. DevOps ⚙️
- 11. SVG Icons using react-native-vector-icons 🐾
- 12. Internationalization 🇮🇳🇺🇸🇷🇺
- 13. Custom Native Modules 🍮
- 14. References
- 15. The End
- Published with GitBook
Android custom native module
Let's say we want to build a native module that gets you the device name.
Before we continue, remember that if you want to write code for Android, you need to open the android project in Android Studio. This is because Android Studio is built for Android development and it will help you resolve all the trivial errors that otherwise would take too much time to resolve.
Let's get started
Open the
./android/project in Android Studio.
Create a Java class file
android/app/src/main/java/com/notetaker/device/DeviceModule.javaThis is our main custom native module file. The custom native module class should extendReactContextBaseJavaModule. After this, we will have to implement thegetName()method.The
getNamemethod basically contains the name by which the module will be exported to the JS.In order to expose a method from a native Java module to Javascript, just write a method and add
@ReactMethodannotation on top of it.These methods can be accessed from
NativeModulesof thereact-nativepackage. See the example below:android/app/src/main/java/com/notetaker/device/DeviceModule.java
package com.notetaker.device; import com.facebook.react.bridge.Callback; import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactApplicationContext; import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactContextBaseJavaModule; import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactMethod; public class DeviceModule extends ReactContextBaseJavaModule { //constructor public DeviceModule(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) { super(reactContext); } //Mandatory function getName that specifies the module name @Override public String getName() { return "Device"; } //Custom function that we are going to export to JS @ReactMethod public void getDeviceName(Callback cb) { try{ cb.invoke(null, android.os.Build.MODEL); }catch (Exception e){ cb.invoke(e.toString(), null); } } }Here we are exporting a method
getDeviceName()from native to Javascript. This method can be accessed in JS viaimport {NativeModules} from 'react-native'; NativeModules.Device.getDeviceName((err ,name) => { console.log(err, name); });NativeModules has a key named 'Device'. This is basically the same name we exported using the method
getName. AndgetDeviceNameis exported because of@ReactMethod.We passed a callback to get the value from the NativeModule.
But creating a module file is not enough. Before a native module can be used we need to register the module. To do this we create another Java class
android/app/src/main/java/com/notetaker/device/DevicePackage.java
package com.notetaker.device; import com.facebook.react.ReactPackage; import com.facebook.react.bridge.JavaScriptModule; import com.facebook.react.bridge.NativeModule; import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactApplicationContext; import com.facebook.react.uimanager.ViewManager; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; public class DevicePackage implements ReactPackage { @Override public List<ViewManager> createViewManagers(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) { return Collections.emptyList(); } @Override public List<NativeModule> createNativeModules( ReactApplicationContext reactContext) { List<NativeModule> modules = new ArrayList<>(); //We import the module file here modules.add(new DeviceModule(reactContext)); return modules; } // Backward compatibility public List<Class<? extends JavaScriptModule>> createJSModules() { return new ArrayList<>(); } }This file just imports our module and instantiates it.
The last step in the registration process is to instantiate our
DevicePackageclass.To do this modify the file
android/app/src/main/java/com/notetaker/MainApplication.java
... ... import com.notetaker.device.DevicePackage; ... ... ... @Override protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() { return Arrays.<ReactPackage>asList( new MainReactPackage(), ... ... new DevicePackage() //Add your package here ); } }; ... ... ...
That's it, let's give it a shot!
In a Javascript file, you can access the module methods using NativeModules.<moduleName>.<methodName>
app/index.js
import {NativeModules} from 'react-native';
...
...
NativeModules.Device.getDeviceName((err, name) => console.log(err, name));
...
...
Running this on an Android emulator returns
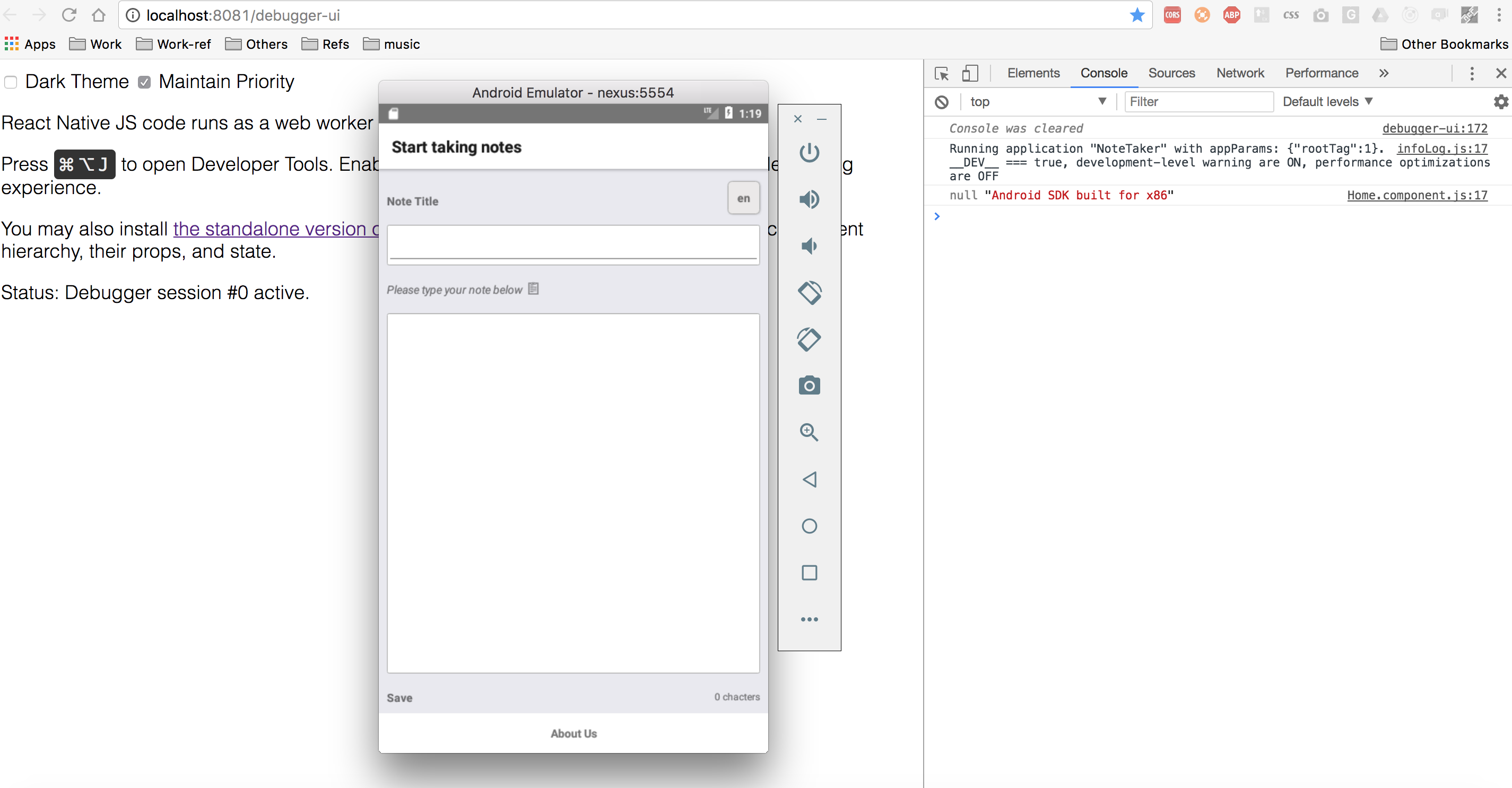
Woot! That was simple!
The code till here can be found on the branch chapter/16/16.1
Note that if you try to build for iOS now, the build will fail as we have not implemented the Device module in iOS yet.